NO. 369, Road S209, Huanxiu, Qingdao City, China
Three-Roller Coating Machine,Aluminate Coupling Agent Modification
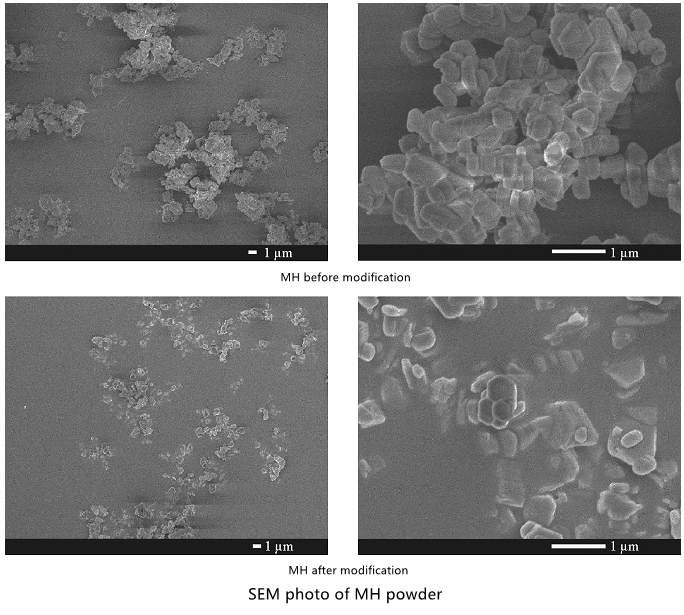
Effects of Aluminate Coupling Agent Modification on Dispersibility and Compatibility of Magnesium Hy
In recent years, halogen-free flame retardants such as magnesium hydroxide (MH), aluminum hydroxide (AH), and aluminum magnesium hydroxide (MAH) have been widely studied due to their green and pollution-free advantages, and their use has also become a trend.Among them, MH is an important additive inorganic flame retardant, which occupies a large proportion in the entire flame retardant market and has a clear growth trend. Its advantages are high stability, low volatility, low flue gas toxicity and low cost. The disadvantage is that the filling amount is large, the binding force with the polymer is small, the compatibility is poor, and the processing and mechanical properties of the polymer are greatly affected. Therefore, it is very necessary to modify the surface of MH powders to improve their dispersibility in polymers. Surface treatment methods using low relative molecular mass coupling agents or surfactants have been found to be quite effective.
Aluminate coupling agent (ACA) is an important surfactant. Usually they are pale yellow to white in color, have high surface reactivity, high decomposition temperature, and are environmentally friendly. ACA has two functional groups, hydrophilic and hydrophobic. The hydrophilic group can chemically react with the polar groups on the MH powder, so that the powder can be grafted with hydrophobic groups, which can greatly reduce the surface energy and improve the MH powder. Compatibility with polymers.
There have been a lot of reports on the surface modification of MH. Commonly used modifiers include fatty acids and their salts, silane coupling agents and titanate coupling agents. Wet surface modification of magnesium hydroxide with (3-oxobutyric acid ethyl ester-O1', O3) bis(propanol-2-radical) alumino-aluminate coupling agent (ACA) by Wang Chen et al. ,the result shows:
1) The characterization results of infrared spectrum, X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetric analysis, scanning electron microscope and energy spectrometer show that the aluminate coupling agent modified magnesium hydroxide successfully and the modification did not destroy the structure of magnesium hydroxide crystals, but only acted on hydrogen At the same time, it was found that the thermal stability of magnesium hydroxide after modification became better. Wet modification of magnesium hydroxide on the surface of aluminate coupling agent can improve the lipophilicity and dispersibility of powder.
2) The tests of sedimentation time, oil absorption rate and suspension viscosity show that the dispersibility and compatibility of modified magnesium hydroxide powder in organic solvent are better than that of unmodified magnesium hydroxide powder.
3) The optimum dosage of aluminate coupling agent to modify magnesium hydroxide powder is 4% of its mass fraction. When the addition amount of aluminate coupling agent is greater than 4%, the modification of magnesium hydroxide powder The effect is not improved, and the dispersibility and compatibility of magnesium hydroxide powder in organic solvents cannot be significantly improved.



Leave a Comment