NO. 369, Road S209, Huanxiu, Qingdao City, China
quartz powder,during grinding,quartz grinding,Quartz Ball Mill Classification Pr
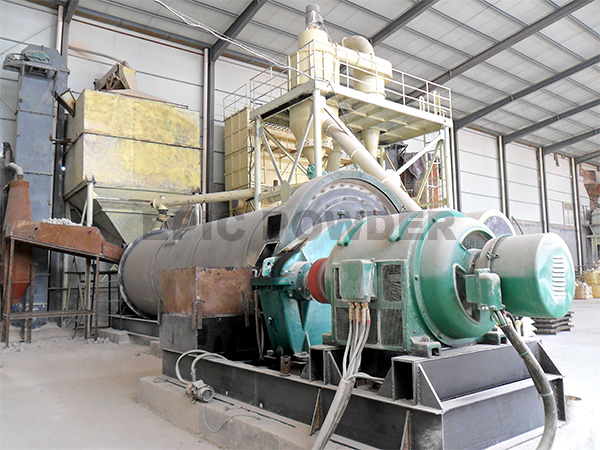

In order to achieve fine quartz powder, some grinding aid is normally added during grinding.
Quartz is hard and not easy to grind, so in quartz grinding, it is difficult to achieve the ideal fineness only by grinding with grinding media. In order to achieve fine quartz powder, some grinding aid is normally added during grinding.Grinding aid is a chemical additive (a gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical) that can greatly improve the grinding efficiency or decrease the consumption of energy and steel when it is added as a grinding aid during the size reduction process. It is generally believed that the addition of grinding aid can decrease the hardness as well as the surface tension of quartz, improve the fluidity of the grinding slurry.
At present, there are mainly triethanolamine, DA dispersant, stearic aid, ammonium chloride, sodium chloride, alcohol, sodium oleate, sodium silicate, dodecylamine for the selection, and application as grinding aid. Besides, fatty alcohol polyoxyethyl ether and trimethyl ammonium chloride are also tested as grinding aid.
Researchers at home and abroad have done some research on the application of grinding aid in quartz grinding, please see as below:
1. Ferric nitrate and potassium xanthate
G.Akdogan and D.Johns believe the density of the grinding aid and the pH value of the pulp has a direct effect on quartz grinding when Ferric nitrate or potassium xanthate is applied as grinding aid.
2. Triethanolamine, glycol
S·Sohon et al. focused on the effects of triethanolamine, ethylene glycol and diethylene glycol, oleic aid, sodium oleate, sulfite waste liquid, and dodecylbenzene sulfonic aid on quartz grinding. It shows that the addition of 0.05% triethanolamine or 0.025% glycol has a little improvement on grinding, while none of them has a great effect on the grinding. In fact, the addition of 0.1% sodium oleate and 0.1% triethanolamine seem to have a negative effect on the grinding of quartz.
3. Alcohol additives
M. Hasegawa et al. made a study of the addition of alcohols with different alkyl groups on quartz ultrafine grinding with a vibrating rod mill in the lab. The results show that alcohol additives are good for quartz ultrafine grinding. The specific surface area of the powder increases with the increase of the additive amount.
4、Ammonium chloride
Liu Fengchun et al. conducted a comparative test of quartz grinding with sodium chloride, ammonium chloride, sodium oleate, and triethanolamine as grinding aid respectively. It shows that when other conditions are the same, ammonium chloride helps a lot on quartz grinding. Proper use of grinding aid will contribute to the production of high output, high efficiency, low energy consumption. Under the same grinding conditions (grinding time is 30min and grinding concentration is 50%), the addition of grinding aid can save the grinding time by more than 50%.
5. Triethanolamine
Hao Baohong et al. focused on the performance of dry grinding, wet grinding, and the addition of triethanolamine as grinding aid in quartz ultrafine grinding. It shows that in terms of improving grinding efficiency, triethanolamine as a grinding aid works better than wet grinding, and wet grinding works better than dry grinding. In terms of crushing limit, dry grinding works better than wet grinding, and wet grinding works better than triethanolamine. The grinding test shows that different grinding conditions have different effects on particle grinding, crystal structure, and chemical bond. Triethanolamine as a grinding aid plays the biggest role in them, then followed by wet grinding, and then dry grinding.
6. Dodecylamine, DA dispersant, sodium silicate, and ammonium chloride
Yin Wanzhong et al. made a study of dodecylamine, DA dispersant, sodium silicate, and ammonium chloride as grinding aid in the ultrafine grinding of SiO2 with a stirring mill. It shows that DA dispersant and sodium silicate have a good performance. With the addition of 1.5% DA dispersant as the optimal dosage, d50 of the product decreased to 0.2860um from 0.3342um, while d97 decreased to 0.5040um from 0.5688.
7. Sodium pyrophosphate
Under the conditions of the mass ratio of quartz to water at 3:7, 0.5% sodium pyrophosphate as grinding aid, and 3 hours of grinding, Wang Yingwei et al. produced the nano-scale ultrafine quartz powder with the particle size less than 60nm with their self-developed centrifugal forced circulation ultrafine grinding machine. The crystallinity of quartz powder is greatly reduced.


Leave a Comment