Key Considerations When Using Talc in Modified Plastics
Talc, a hydrated magnesium silicate, belongs to the “phyllosilicate” class with a trihedral three-layer structure. Its structure comprises a brucite layer (magnesium hydroxide, MgO·H2O) sandwiched between two silicon dioxide (SiO2) layers. These layers are held together by weak van der Waals bonds, making them prone to sliding and separation under shear.
Talc Powder Characteristics:
1. Hardness: Talc is one of the softest minerals, with a hardness of 1 (compared to calcite’s 3). Commercial talc is harder due to impurities like calcite and tremolite.
2. Color: Raw talc varies in color—white, gray, yellow, blue, light green, pink, and brown. After processing, it typically becomes a powder ranging from gray to white with varying degrees of luster.
3. Particle Size and Shape: Talc used as a filler is usually very fine. Suppliers can adjust particle size through processing. Talc crystals can be flake, leaf, needle, or block-shaped, with most domestic products being flake-shaped. The aspect ratio (diameter-to-thickness) is key to talc’s performance.
4. Surface Properties: Talc’s surface properties vary by source, affecting specific surface area and oil absorption, which in turn influence product fineness. Its lamellar structure typically results in a large specific surface area.
5. Electrical and Thermal Properties: Talc is an electrical insulator and stable at high temperatures (up to 900°C). It has low thermal conductivity and high thermal shock resistance. When heated above 800°C, talc loses its bound crystalline water and decomposes into enstatite through an endothermic reaction.
6. Optical Properties: Pure talc has three refractive indices: X=1.539, Y=1.589, and Z=1.589, with a small, variable optical axis angle. This allows talc to alter the direction of sunlight, converting direct light into scattered light, enhancing the thermal insulation of agricultural greenhouse films.
7. Supply Sources of Talc Powder: In China, talc resources are primarily found in Guilin (Guangxi), Qixia (Shandong), the Jiaodong Peninsula, Laizhou, and Haicheng (Liaoning). Talc from Guangxi is known for its transparency and excellent processing performance. Shandong’s talc has good whiteness but poor transparency due to low SiO2 content. Haicheng’s talc is abundant, moderately priced, and available in various grades. When selecting talc, it’s important to choose the appropriate specifications based on the intended use.
8. Talc as a Reinforcing Filler: Talc’s flake structure makes it a valuable reinforcing material in plastics. Commercial talc, finely crushed, improves mechanical properties when evenly distributed in resin, similar to how metal supports enhance cement parts. Its low cost makes it a suitable extender, while its flake configuration or high aspect ratio enhances the composite’s mechanical strength.
Talc Requirements for Transparent Modified Masterbatch
High-quality, ultra-fine talc with a flaky structure serves as a reinforcing and modifying functional filler in plastics. It reduces resin usage while significantly improving stiffness, impact strength, bending modulus, and thermal stability. Talc’s even dispersion in resin creates a reinforced support structure with excellent mechanical properties, while also enhancing thermal insulation and barrier properties.
Key quality indicators for industrial talc powder include purity, whiteness, and fineness, all of which should be considered together to assess product quality.
The higher the purity of talc, the better its reinforcing effect. Impurities, particularly metal minerals like iron, can negatively impact the aging resistance of plastics. The silicon (SiO2) content in talc is a key indicator of its grade. Higher silicon content correlates with higher purity, better performance, and a higher price. Talc selection should align with the performance requirements of specific plastic products.
For instance, high-silicon talc enhances the light transmittance, tensile strength, breaking strength, and puncture resistance of agricultural films. In contrast, injection molding, plates, and rods do not require high silicon content; lower-silicon talc is less expensive and can improve hardness and impact strength.
The effect of SiO2 content in talcum powder on the performance of talcum powder can be seen in Table
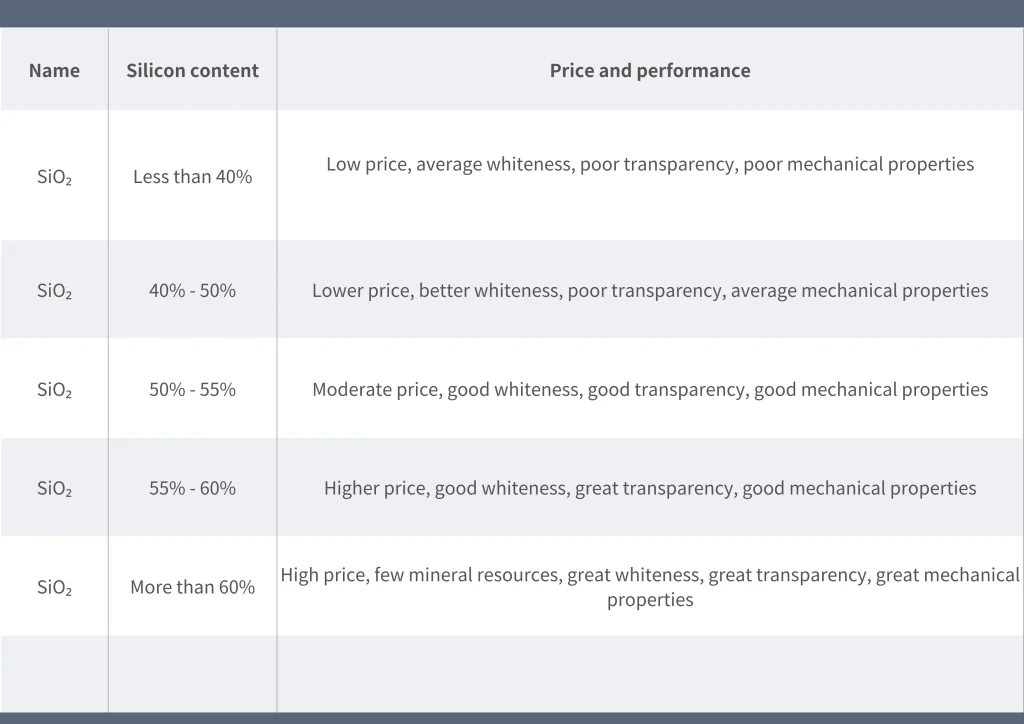
The reinforcing effect of talc in plastic products is primarily due to its unique flaky structure. Maintaining this structure during micronization is crucial for maximizing its benefits. Factors like specific surface area, oil absorption, particle shape, and size also influence the performance of modified masterbatches. While these properties have been covered in detail, further exploration and practical experience are necessary to optimize talc’s application.
Talc transparent modified masterbatch production and mixing process
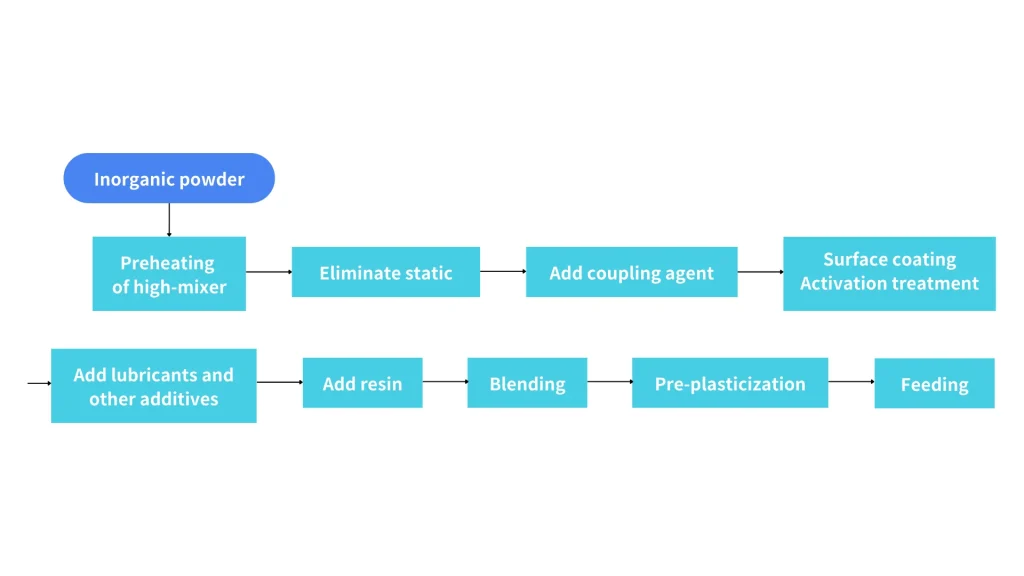
Talc transparent modified masterbatch production extrusion granulation mixing process
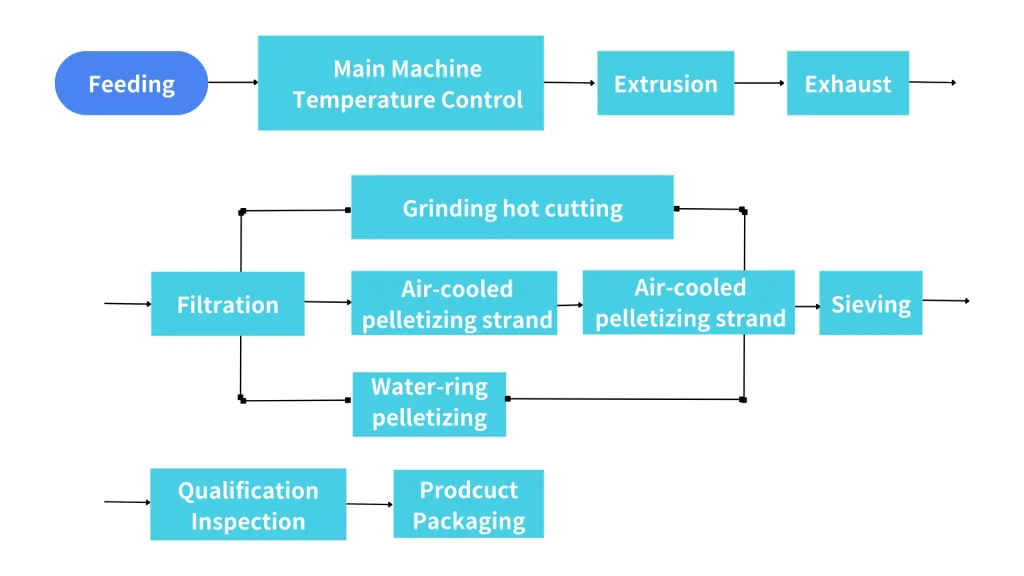
Talc is an important inorganic material for plastic filling modification. It has been widely used in polypropylene modification at home and abroad. It is mainly used to produce automotive parts, front and rear bumpers, instrument panel panels, interior decorative panels, etc.; it is also used in the home appliance industry, such as washing machine parts, air conditioning parts, TV back shells, electric heater shells and various daily home appliance shells.
If you would like to know more about jet mills that can process talc, please contact Epic Powder for more information.








